Introduction to Zero Trust Architecture
The current digital era, marked by an exponential increase in cyberattacks, requires companies to rethink their cybersecurity strategies. In this context, Zero Trust architecture emerges as a robust and adaptive response to complex and constantly evolving threats. This section explores the foundations and relevance of Zero Trust, highlighting why this approach is crucial for cloud and hybrid environments, including those managed through Microsoft solutions.
Foundations of Zero Trust and relevance for Microsoft solutions
The concept of Zero Trust is based on a fundamental maxim: "Never trust, always verify." This approach breaks with the traditional model of "trust but verify" , where internal systems are considered reliable by default. Zero Trust, on the other hand, treats all users and devices, internal or external, with the same level of skepticism, requiring rigorous authentication and continuous validation.
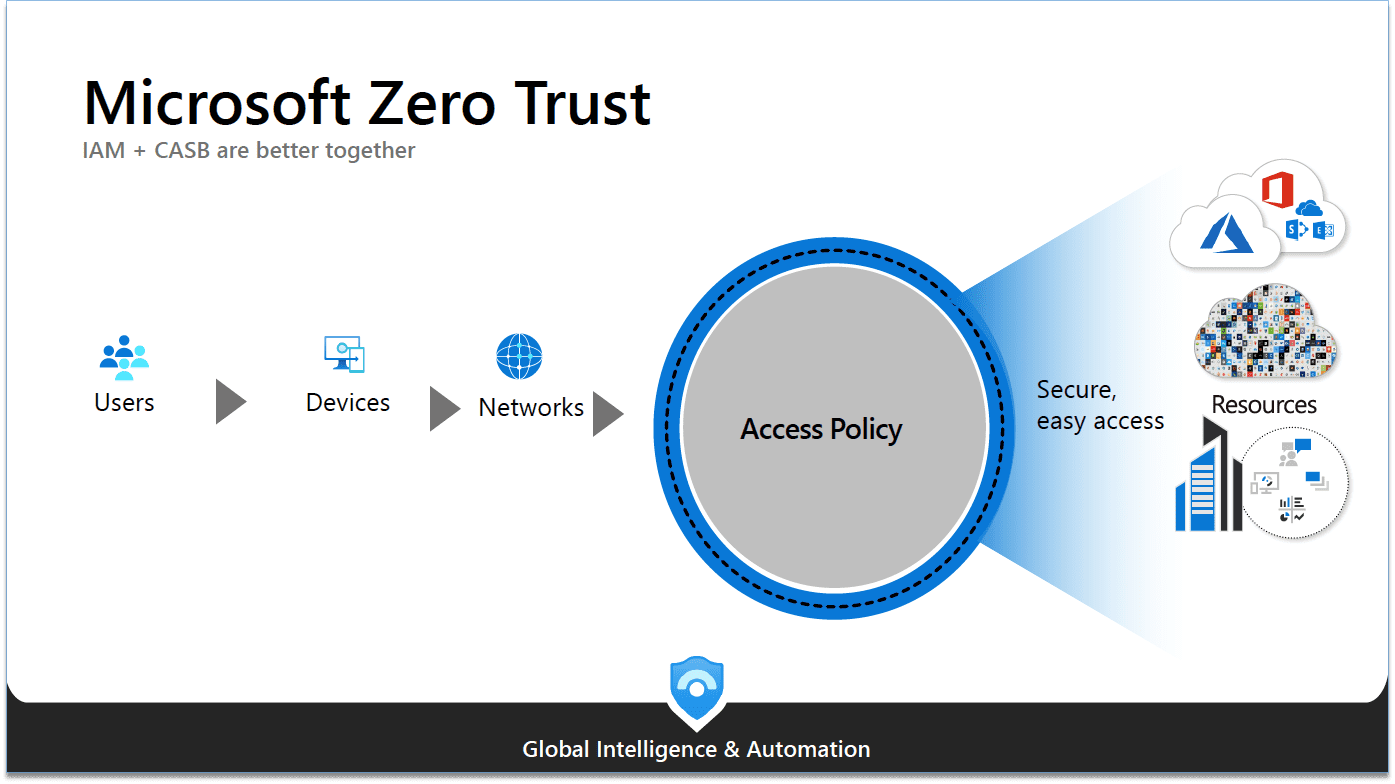
Why Zero Trust is crucial for Cloud and Hybrid environments
With the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, like those offered by Microsoft, traditional security perimeters are becoming obsolete. Cloud and hybrid solutions require a security approach that can dynamically adapt to different environments and access conditions. Zero Trust offers this flexibility, aligning perfectly with the intrinsic characteristics of the Cloud: accessibility, mobility and interconnectivity.
I - Functional principle of Zero Trust architecture adapted to Microsoft solutions
Zero Trust architecture is not a single product but a set of security principles that can be applied to various environments, including those based on Microsoft solutions. In this section, we'll explore how Zero Trust adapts to the specifics of Microsoft solutions, providing improved security and more effective risk management.
Application of the principle “Never trust, always verify”
Zero Trust boils down to a simple but powerful security policy: “Never trust, always verify.” This means that every request for access to a network or resource must be rigorously authenticated, authorized and encrypted, regardless of its source. In the Microsoft ecosystem, this involves deep integration with solutions like Azure Active Directory for identity and access management, and Azure Information Protection for data protection.
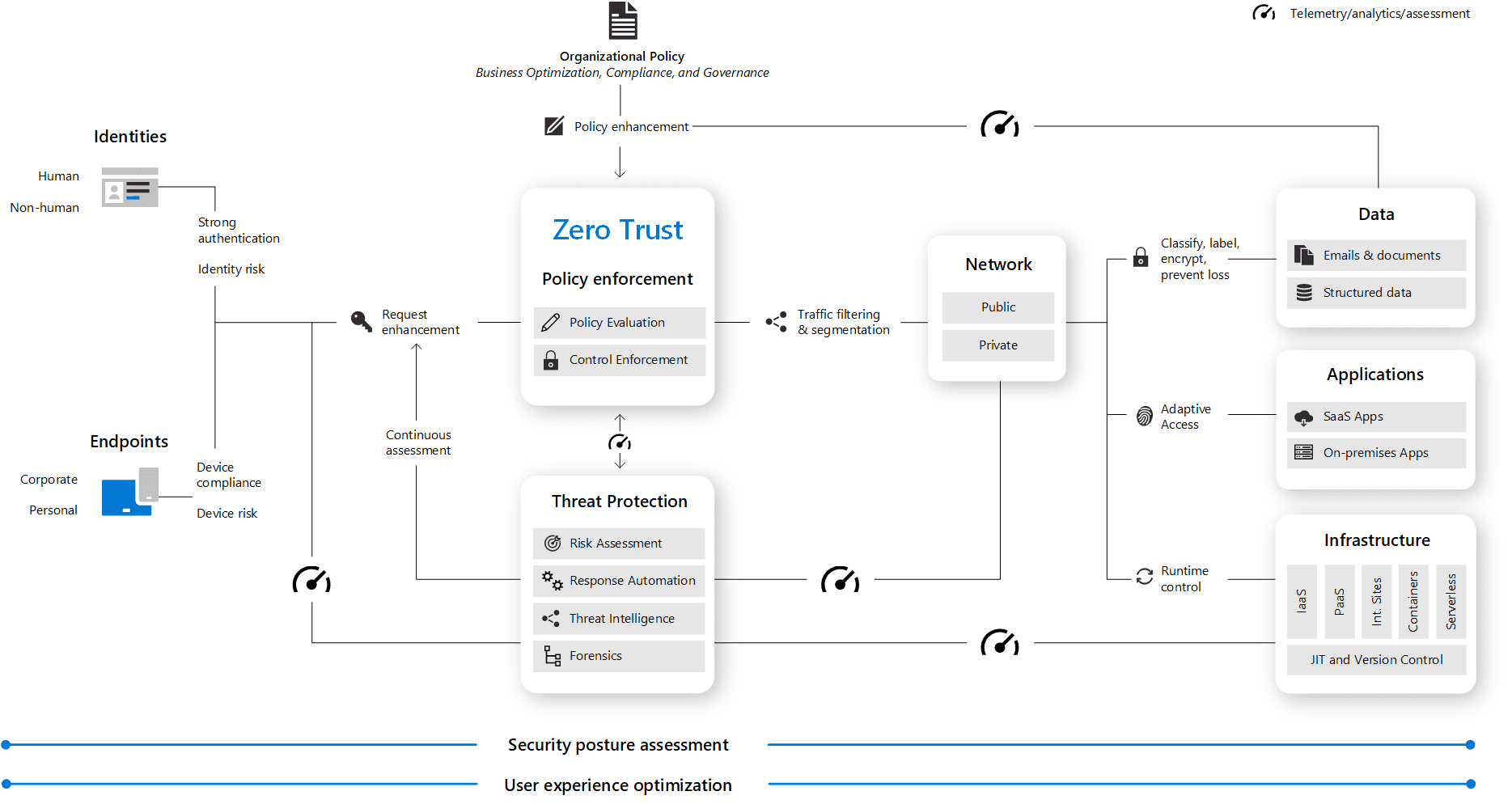
Key components of Zero Trust
Applying Zero Trust to Office 365 and Microsoft 365 focuses on three main areas: user identities, the devices used to access resources, and the applications themselves . Each component plays a key role in securing the environment.
Identity and access management
Implementation of multi-factor authentication policies, identity and privileged access management.
Device security
Ensure that only secure and compliant devices can access company resources
II - Implementing Zero Trust in your company
Implementing Zero Trust architecture in an enterprise, especially for those using Microsoft solutions, is a crucial strategic process to strengthen security while optimizing performance This section details the key steps and considerations needed to effectively plan and deploy Zero Trust in your IT environment.
Assessment of specific needs
The first step toward implementing Zero Trust is a thorough assessment of the company's current IT environment, with a particular focus on Microsoft applications. This assessment should focus on:
Application and data auditing
Identify where critical data is stored and how it is accessed through Microsoft applications such as Dynamics 365, Power BI, Azure IAAS and PAAS.
Analysis of access patterns
Understand how users, both internal and external, access Microsoft resources.
Compliance and risk assessment
Determine regulatory requirements and identify security risks specific to Microsoft solutions.

Zero Trust deployment strategies with Microsoft solutions
After assessing the needs, the next step is to plan and execute the Zero Trust deployment. For businesses using Microsoft solutions, this means:
Setting strict access policies
Implement detailed access policies for applications like Dynamics 365 and Power BI, based on user roles and responsibilities.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Strengthen credential security, especially for mission-critical applications like Azure IAAS and PAAS.
Securing network connections
Use tools like Azure Active Directory to create secure, monitored network connections.
III - Benefits and challenges of adopting Zero Trust
Adopting Zero Trust architecture offers many benefits, but it also presents unique challenges. Understanding these aspects is essential for businesses considering implement this cybersecurity strategy. This section explores the key benefits of Zero Trust and the potential obstacles to overcome.
Enhanced security and risk reduction
The main advantage of Zero Trust architecture is the significant improvement in security. By adopting this approach, businesses benefit from:
Improved access control
Zero Trust minimizes the risk of unauthorized access by requiring continuous authentication and verification for every user and device, thus reducing the chances of data compromise.
Adaptability to emerging threats
The dynamic nature of Zero Trust allows businesses to quickly adapt to new threats, providing proactive protection against ever-evolving cyberattacks.
Regulatory conformity
With stricter security standards, Zero Trust helps businesses comply with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, by ensuring security and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Impact on collaboration and mobility in the Microsoft ecosystem
Implementing Zero Trust directly influences how businesses use Microsoft solutions for collaboration and mobility:
Securing collaborative environments
With Zero Trust, applications like Microsoft Teams and SharePoint become more secure, enabling risk-free collaboration between users, even when they're on the move.
Secure mobile access
Zero Trust facilitates secure access to corporate resources from any device, crucial for hybrid and mobile work environments.
Identity and access management
Zero Trust integration with Azure Active Directory improves identity and access management, a key element for secure mobility and collaboration.

Conclusion: Zero Trust, a strategic lever
Adopting Zero Trust architecture is more than just a security update; it constitutes an essential strategic lever for businesses in the modern digital landscape. This conclusion summarizes the key points covered in the article and highlights the future prospects of Zero Trust, particularly in relation to Microsoft solutions.
Integrate Zero Trust into an overall security strategy
Zero Trust is not an isolated solution but a paradigm shift in the way we think about IT security.
By adopting Zero Trust, companies do not just strengthen their security; they adopt a proactive posture, adapting to constantly evolving digital threats.
This approach aligns security with business objectives, ensuring robust protection of data and infrastructure critical while supporting agility and innovation.
Implementing Zero Trust, especially in environments using Microsoft solutions, provides deep compatibility and integration with existing systems. This enables a smooth transition to a more resilient security architecture, while fully leveraging the capabilities of Microsoft solutions for collaboration, mobility and the cloud.
Future perspectives and evolution of Zero Trust in the Microsoft ecosystem
The future of Zero Trust is intrinsically linked to evolving technology and cybersecurity threats. With the increasing adoption of cloud, AI and IoT, Zero Trust will become an even more crucial standard. For businesses using Microsoft solutions, this means even deeper integration of Zero Trust into services like Azure, Office 365, and Microsoft 365.
The focus will be on developing advanced, automated, artificial intelligence-based security solutions to anticipate and respond to threats more effectively.